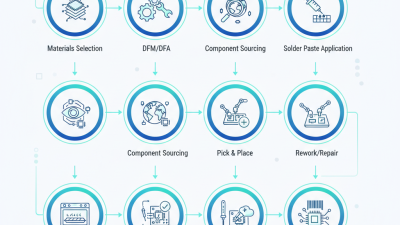
In the ever-evolving landscape of electronics manufacturing, techniques in PCB assembly are advancing rapidly. Industry expert John Smith, a leader in PCB technology, once noted, “Innovation in PCB assembly drives the future of electronics.” His insight emphasizes the critical role of PCB assembly in creating efficient, high-quality electronic products.
Today's PCB assembly methods focus on automation, improved design, and sustainability. Companies are adopting advanced machinery to enhance precision and speed. However, the push for innovation sometimes overlooks quality control. It’s essential to balance speed with meticulous assembly processes. Some manufacturers face struggles due to a lack of skilled technicians. High-quality assembly requires not just technology, but expertise.
Emerging trends like IoT and AI integration are reshaping the PCB assembly landscape. Smart manufacturing is on the rise, yet it also presents challenges. As companies chase efficiency, they must evaluate the implications of these technologies. It is crucial to avoid becoming overly reliant on automation. The human element remains vital in ensuring quality and innovation in PCB assembly.

In 2026, the landscape of PCB assembly is set to evolve dramatically. Innovative techniques enhance efficiency and reduce costs. According to the IPC’s 2023 outlook, automated processes can increase production efficiency by up to 30%. This significant boost allows manufacturers to meet rising global demands swiftly.
Adopting advanced robotics in assembly lines is one key trend. These machines perform tasks with precision and speed. Yet, not all companies have made this transition smoothly. Many lack the necessary training and resources for integration, leading to implementation challenges.
Tip: Invest in training programs for your team to navigate these new technologies. Upgrading software and machinery may appear costly initially. However, the long-term savings and efficiency gains often justify the investment.
Another notable trend is the shift towards environmentally friendly materials. Manufacturers face pressure to reduce their carbon footprint. However, the transition can be imperfect. Many are uncertain about sourcing sustainable materials while maintaining quality standards.
Tip: Conduct thorough research on suppliers to find reliable materials. Be prepared for trial and error as you adjust your supply chains. This approach may lead to more sustainable practices over time. Embrace change, but understand that it takes time to perfect.
The landscape of surface mount technology (SMT) is evolving rapidly. According to a recent IPC report, the SMT market is projected to grow by over 7% annually. This growth is driven by the increasing demand for compact electronic devices. Smaller components require precise assembly techniques. The challenge lies in meeting these demands without compromising quality.
Advanced soldering methods are gaining traction. Processes like selective soldering and vacuum reflow are becoming standard. These techniques enable manufacturers to reduce defects while adhering to tighter tolerances. However, many companies still struggle with process optimization. Nearly 30% of manufacturers reported issues with defect rates exceeding acceptable levels. This highlights a need for continuous improvement in assembly practices.
The trend toward automation in SMT has gained momentum. Automated processes can enhance efficiency and accuracy. Yet, the initial investment remains a concern for some. Many manufacturers are hesitant to adopt full automation. The balance between human oversight and machine efficiency is still being navigated. This need for reflection on automation's role will shape SMT strategies in the next few years.
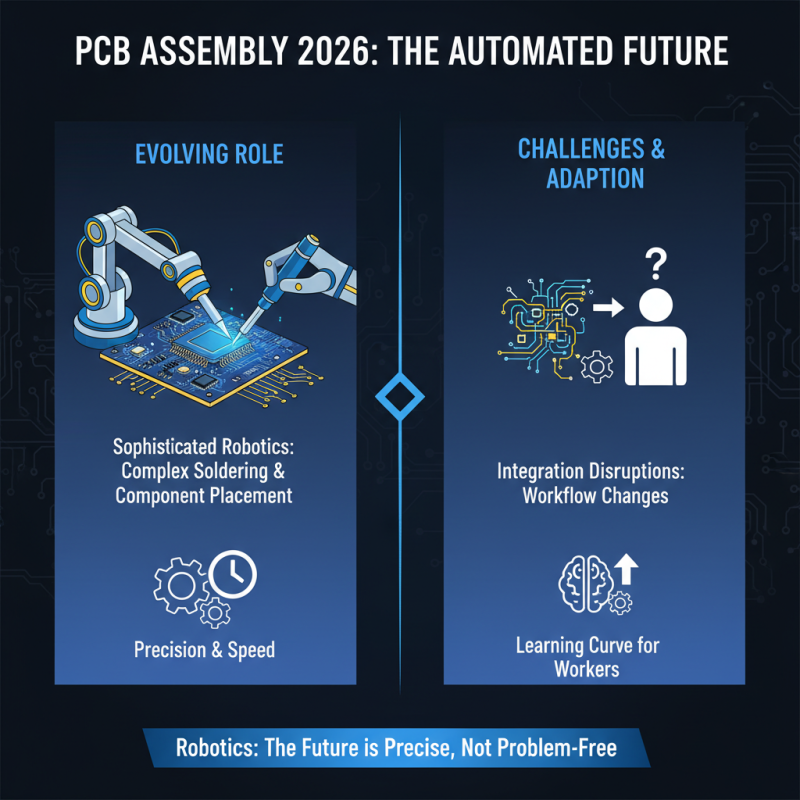
The role of automation and robotics in PCB assembly is rapidly evolving. In 2026, we see more sophisticated robotics taking over complex tasks. These robots can handle intricate soldering and component placement with precision. However, they are not without challenges. Integrating these machines into existing workflows can disrupt traditional processes. This leads to a learning curve for workers who may struggle with new technology.
Moreover, while automation increases efficiency, it also raises concerns about quality control. Errors can occur if machines are not correctly calibrated. Human oversight remains essential, and finding the right balance between automation and manual processes is critical. Some companies may rush into full automation, only to face unforeseen issues later.
Innovation in robotics is promising, but it’s essential to reflect on potential pitfalls. Every technological advance comes with its own set of challenges. As the industry moves forward, embracing both the benefits and the risks will shape the future of PCB assembly. Adapting to these changes is a continuous journey.
Sustainability has become a central focus in PCB manufacturing. The industry is increasingly adopting eco-friendly materials and practices. According to a recent industry report, 70% of manufacturers now prioritize sustainable sourcing. This shift reduces the environmental impact significantly.
Moreover, companies are implementing waste reduction strategies. For instance, more facilities use recycle-friendly materials. Some have also minimized hazardous waste by 50% over the last five years. However, challenges remain. Not all manufacturers can afford new technologies. Many still rely on traditional methods, which are less sustainable.
Energy efficiency is another key area. The latest data indicate that energy-efficient processes can reduce costs by up to 30%. Yet, not every company invests in upgrading their systems. There is a gap between intention and action. The push for sustainability needs to align with economic realities. Innovation is essential, but it often encounters resistance.
The electronics industry faces challenges in PCB assembly.
As technology advances, manufacturers must adapt to new demands.
Miniaturization is one key trend.
Components are getting smaller, creating assembly difficulties. Managing placement accuracy is vital.
Inadequate precision can lead to costly failures.
Manufacturers should focus on automation.
This can improve speed and reduce errors. However, integrating machinery is complex.
Staff need proper training for new systems. Trade-offs exist between speed and quality.
Rushing through assembly can compromise product reliability.
Tips:
Regular audits can identify weaknesses in processes.
Emphasizing continuous training helps staff adapt.
Collaboration between teams fosters better solutions.
Addressing these challenges will enhance productivity in PCB assembly.
This requires open-mindedness and acceptance of mistakes. Embrace a mindset of learning and adaptation.